Direct-zol RNA Purification Kits
You're closer than you think to an easier workflow. The Direct-zol RNA kits provide a streamlined method for the purification of high-quality RNA directly from samples in TRI Reagent® or similar in just 7 minutes, transforming your lab efficiency.
Reduce time to accelerate tomorrow's discoveries. Simply apply a prepared sample in TRI Reagent® directly to the Zymo-Spin Column and then bind, wash, and elute the RNA. No phase separation, precipitation, or post-purification steps are necessary.
Watch the video to learn more.
- Higher miRNA Recovery
- No Precipitation or Phase Separation
- Compatible with Existing Workflows
- The Only Automated Solution
- Trusted by Leading Institutions
Higher miRNA Recovery
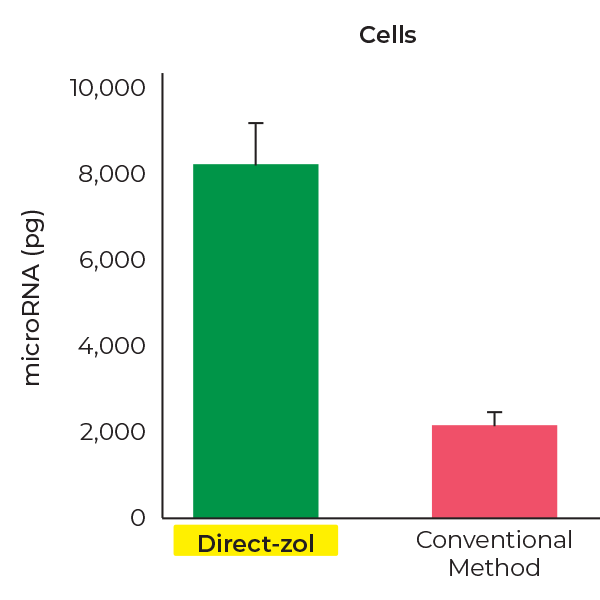
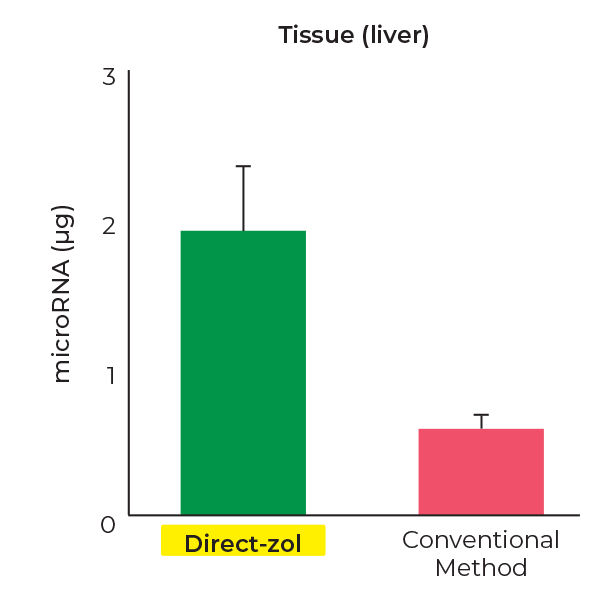
Direct-zol RNA kits recover ~4-fold more miRNAs(< 40 nt) than conventional methods.
No Chloroform. No Precipitation. No Phase Separation!
Direct-zol: 7 minutes
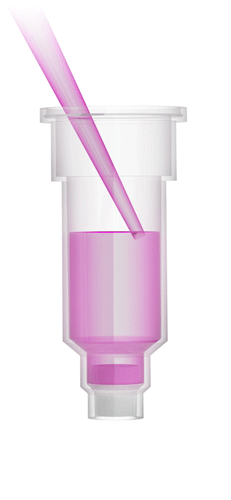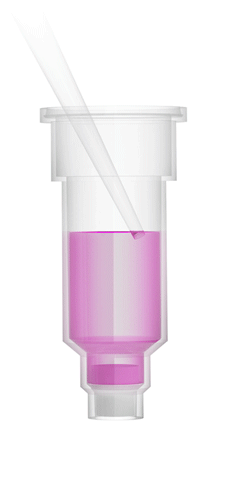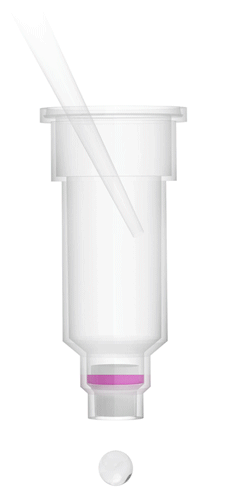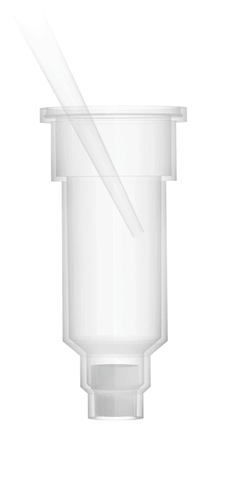
Conventional Method: 90+ minutes
Workflow and Compatibilities
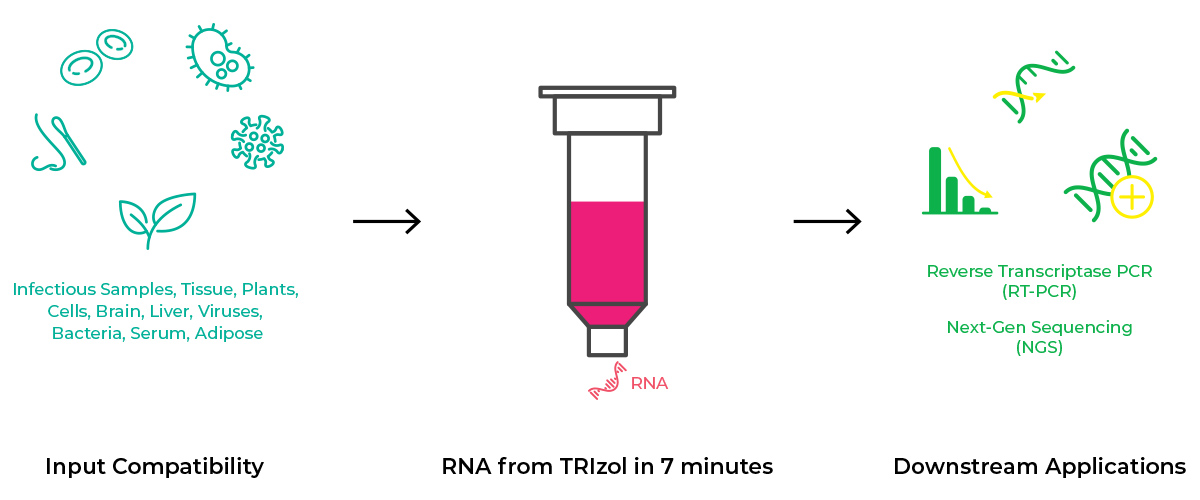
The Only Automated Solution for TRI Reagent®(s) Samples
High Quality, NGS-Ready RNA
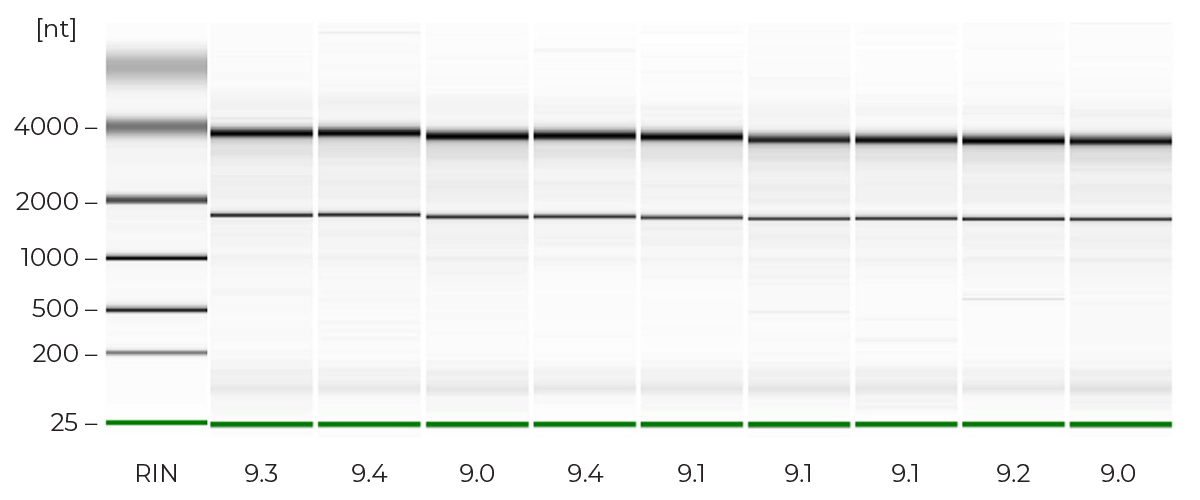
The Direct-zol-96 MagBead RNA method eliminates traditional chloroform, phase separation, and preciptiation steps, enabling a fully automatable TRI Reagent®(s) extraction. Just add ethanol to any TRI Reagent®(s) sample, bind to magnetic beads, wash, and elute NGS-ready RNA.
Trusted by Leading Institutions
Citations
- Sir Karakus, G., Tastan, C., Dilek Kancagi, D. et al. Preclinical efficacy and safety analysis of gamma-irradiated inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidates. Sci Rep 11, 5804 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-83930-6.
- Suntsova, M., Gaifullin, N., Allina, D. et al. Atlas of RNA sequencing profiles for normal human tissues. Sci Data 6, 36 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-019-0043-4.
- Ramos-Mandujano, G., Salunke, R., Mfarrej, S., Rachmadi, A. T., Hala, S., Xu, J., … Li, M. (2021). A Robust, Safe, and Scalable Magnetic Nanoparticle Workflow for RNA Extraction of Pathogens from Clinical and Wastewater Samples. Global Challenges, 2000068. doi:10.1002/gch2.202000068.
- Christina Chuong, Tyler A. Bates, James Weger-Lucarelli, Infectious cDNA clones of two strains of Mayaro virus for studies on viral pathogenesis and vaccine development, Virology, Vol 535, 2019, Pages 227-231, ISSN 0042-6822, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2019.07.013.
- Christopher Smith, Nural Cokcetin, Thuyen Truong, Elizabeth Harry, Gyorgy Hutvagner, Sarah Bajan, Cataloguing the small RNA content of honey using next generation sequencing, Food Chemistry: Molecular Sciences, Volume 2, 2021, 100014, ISSN 2666-5662, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fochms.2021.100014.
- Ren, Li-Li; Wang, et. al. Identification of a novel coronavirus causing severe pneumonia in human: a descriptive study, Chinese Medical Journal: May 5, 2020 - Volume 133 - Issue 9 - p 1015-1024 doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000722.
- Patricia Angélica Barril, Luis Alfredo Pianciola, Melina Mazzeo, María Julia Ousset, María Virginia Jaureguiberry, Mauricio Alessandrello, Gloria Sánchez, Juan Martín Oteiza, Evaluation of viral concentration methods for SARS-CoV-2 recovery from wastewaters, Science of The Total Environment, Volume 756, 2021, 144105, ISSN 0048-9697, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144105.
Which Direct-zol RNA Kit is Right for You?
Get Your Free Sample
Need help? Contact Us

















 Direct-zol
Direct-zol  Direct-zol Miniprep
Direct-zol Miniprep
 Direct-zol Microprep
Direct-zol Microprep
 Direct-zol-96
Direct-zol-96 Direct-zol-96 MagBead RNA
Direct-zol-96 MagBead RNA
