Unlocking the Potential for Clinical DNA Methylation Applications
The Evolution of Bisulfite Conversion Technology
Introduction
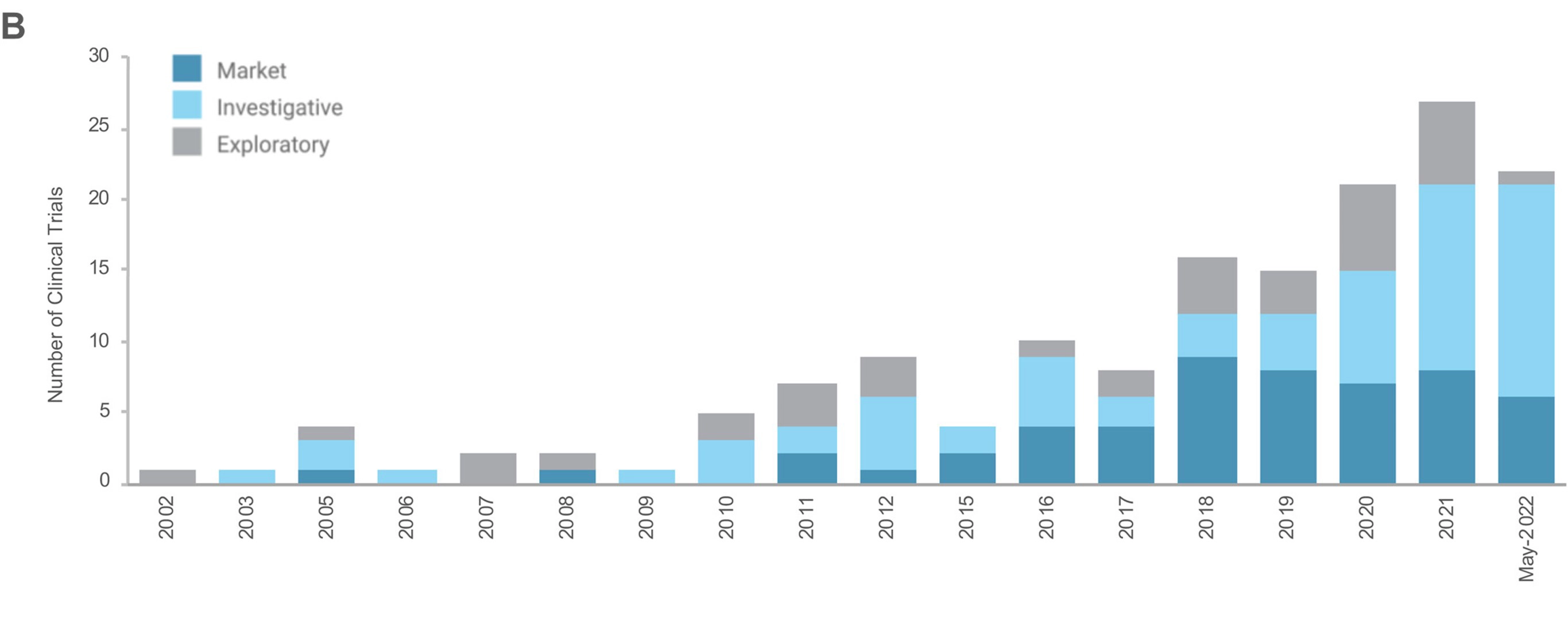
Bisulfite treatment is regarded as the gold standard for DNA methylation analysis. The technique has been extensively validated and is known for its reliability, reproducibility, and cost-effectiveness, leading to its widespread adoption in both research and clinical settings.1-2 Clinical trials involving DNA methylation-based strategies have significantly increased in last ten years, with over 30 DNA methylation-based assays already aiding clinical decision-making in cancer.3 Moreover, DNA methylation-based clinical assays are being developed for applications beyond cancer, including environmental and occupational exposures, aging, metabolic diseases, and other chronic conditions. As the demand for DNA methylation-based molecular tests in clinical applications continues to grow, researchers are striving to refine bisulfite protocols to address challenges such as excessive DNA fragmentation and time-consuming conversion steps.4
Empowering clinical Analysis with the EZ DNA Methylation-Lightning™ Kit for fragmented samples
The EZ DNA Methylation-Lightning™ kits have been specifically engineered to meet modern challenges. Zymo scientists have developed an innovative conversion chemistry that utilizes gentler reaction conditions to preserve DNA integrity; additionally, the conversion workflow has been streamlined to take as little as one hour. With our proprietary engineering and manufacturing technologies, the EZ DNA Methylation-Lightning™ Kit has proven its ability to recover fragments over 50 bp while maintaining a conversion efficiency greater than 99%. The kit excels not only in speed but also in minimizing degradation, a crucial factor when working with fragmented or deteriorated DNA samples.
For example, formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue, a common clinical sample type in biorepositories, preserves the sample but is also known to cause DNA fragmentation and degradation. The ability to recover high-quality genetic and epigenetic information from these samples is critical for cancer research, specifically for the discovery of novel biomarkers that enhance early disease detection.5 The EZ DNA Methylation-Lightning™ Kit stands out for its ability to handle these challenging samples. Its specialized conversion process ensures that even DNA from problematic or degraded samples can be effectively recovered and analyzed.6-12
For instance, methylation-specific PCR (MSP) was performed with FFPE DNA that was purified using the Quick-DNA FFPE Miniprep Kit (D3067), converted using the EZ DNA Methylation-Lightning™ Kit (D5030), and then PCR amplified with methylation-specific primers for several cancer biomarkers (Figure 2). This demonstrates that the modified bisulfite conversion protocol is compatible with and recovers sufficient DNA from fragmented or degraded samples such as FFPE DNA to be amplified by targeted PCR-based approaches.

Empowering Analysis with the EZ DNA Methylation-Lightning™ Kit for Scarce Samples
For scientists and researchers, especially those working with limited DNA samples such as cell-free DNA or DNA from early embryonic development, losing a significant portion of DNA could result in missing out on crucial information. By choosing a method like the EZ DNA Methylation-Lightning™ Kit, which maximizes DNA recovery, researchers can ensure more reliable results from their studies. This insight is invaluable for advancing research in genetics, medicine, and forensics, where precision and efficiency are paramount.
Beyond the other technical advancements of the EZ DNA Methylation-Lightning™ Kit, one of its most overlooked features is the straightforward procedure. The ready-to-use conversion reagent is added directly to the DNA, and bisulfite conversion starts immediately. The minimized steps for tube transferring and clean-up ensure the highest efficiency in recovering converted DNA.
A comparison study of different conversion kits was conducted by Hong et al.13 As the data shows, the EZ DNA Methylation-Lightning™ Kit emerged as the most efficient, boasting the highest recovery rate. In contrast, enzymatic conversion protocols require bead purification twice, which can reduce recovery rates and introduce increased operational complexity and variability between batches. Additionally, the reduced recovery rate can vary greatly depending on the skill with which a researcher executes the procedure. The stark difference in recovery rates between these kits underscores the importance of selecting an optimal conversion protocol.

Future Directions
For routine clinical operations, achieving a fast turnaround time is essential to provide timely information for clinical decisions. The diversity of clinical sample types and the variable integrity of DNA add complexity to this process. Therefore, as bisulfite conversion technology becomes more integrated into diagnostic and clinical settings, the utilization of Zymo Research's innovative EZ DNA Methylation™ Lightning Kit addresses the pressing need for high-throughput methods to expedite turnaround times and ensure sample fidelity for robust analytics and reporting.
With the continuing decrease in Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) costs and the exponential growth of computational power, the use of whole methylome profiling in clinical applications is becoming more prevalent. Zymo Research has developed many NGS library preparation kits featuring the state-of-the-art EZ DNA-Methylation™ Lightning bisulfite conversion technology. The effectiveness and efficiency of Zymo Research's solutions for DNA methylation underscore their pivotal role in advancing research, making them indispensable tools for scientists aiming to unravel the mysteries of the natural world.
Discover Zymo Research’s DNA methylation technologies:
References
- Patterson K, Molloy L, Qu W, Clark S. DNA methylation: bisulphite modification and analysis. J Vis Exp. 2011. doi:10.3791/3170.
- Clark SJ, Statham A, Stirzaker C, Molloy PL, Frommer M. DNA methylation: bisulphite modification and analysis. Nat Protoc. 2006;1:2353–64.
- Davalos, Veronica, and Manel Esteller. "Cancer epigenetics in clinical practice." CA: a cancer journal for clinicians 73.4 (2023): 376-424.
- Jung M, Uhl B, Kristiansen G, Dietrich D. Bisulfite Conversion of DNA from Tissues, Cell Lines, Buffy Coat, FFPE Tissues, Microdissected Cells, Swabs, Sputum, Aspirates, Lavages, Effusions, Plasma, Serum, and Urine. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1589:139-159. doi: 10.1007/7651_2015_260.
- Steiert, Tim A., et al. "A critical spotlight on the paradigms of FFPE-DNA sequencing." Nucleic Acids Research 51.14 (2023): 7143-7162.
- Araújo, Oscar C., et al. "RASSF1A and DOK1 promoter methylation levels in hepatocellular carcinoma, cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic liver, and correlation with liver cancer in Brazilian patients." PloS one 11.4 (2016): e0153796.
- Bosch, Dustin E., et al. "Isolated MLH1 loss by immunohistochemistry because of benign germline MLH1 polymorphisms." JCO precision oncology 6 (2022): e2200227.
- Moran, Bruce, et al. "Assessment of concordance between fresh-frozen and formalin-fixed paraffin embedded tumor DNA methylation using a targeted sequencing approach." Oncotarget 8.29 (2017): 48126.
- Moran, Bruce, et al. "Assessment of concordance between fresh-frozen and formalin-fixed paraffin embedded tumor DNA methylation using a targeted sequencing approach." Oncotarget 8.29 (2017): 48126.
- Hirai, Ryosuke, et al. "Methylation analysis of DCC gene in saliva samples is an efficient method for non-invasive detection of superficial hypopharyngeal cancer." British Journal of Cancer (2024): 1-7.
- Popa, Horia, et al. "Pillar Biosciences oncoReveal TM methylQuant Panels: Accurate and easy-to-use methylation NGS assays leveraging SLIMamp technology." (2023).
- Dopeso, Higinio, et al. "Genomic and epigenomic basis of breast invasive lobular carcinomas lacking CDH1 genetic alterations." NPJ Precision Oncology 8.1 (2024): 33.
- Hong, Sae Rom, and Kyoung-Jin Shin. "Bisulfite-converted DNA quantity evaluation: a multiplex quantitative real-time PCR system for evaluation of bisulfite conversion." Frontiers in genetics 12 (2021): 618955.


